以下笔记内容均为Windows版本。
本篇笔记跟踪记录了Chromium的启动过程,主要关注 Browser 进程和 Renderer 进程。根据 Chromium 项目的分层设计,我们把 Content API 称作为 Content 层,而把调用 Content API 实现浏览器程序的部分称作为 Embedder 层。在项目中,Embedder 层有 chrome、content_shell 等多种实现。
1、main() 函数 Chromium的main函数在 chrome\app\chrome_exe_main_win.cc,具体如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #if !defined(WIN_CONSOLE_APP) int APIENTRY wWinMain (HINSTANCE instance, HINSTANCE prev, wchar_t *, int ) #else int main () HINSTANCE instance = GetModuleHandle (nullptr ); #endif install_static::InitializeFromPrimaryModule (); SignalInitializeCrashReporting (); ...... VLOG (1 ) << "About to load main DLL." ; MainDllLoader* loader = MakeMainDllLoader (); int rc = loader->Launch (instance, exe_entry_point_ticks); loader->RelaunchChromeBrowserWithNewCommandLineIfNeeded (); delete loader; return rc; }
在main函数中,最重要的一步,就是 int rc = loader->Launch(instance, exe_entry_point_ticks); 载入 chrome.dll运行。
2、载入 chrome.dll 在这里首先调用了 MakeMainDllLoader() 函数,这是一个静态函数,在chrome\app\main_dll_loader.cc 中,内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 MainDllLoader* MakeMainDllLoader () {#if defined(GOOGLE_CHROME_BUILD) return new ChromeDllLoader (); #else return new ChromiumDllLoader (); #endif }
函数创建并返回一个 ChromiumDllLoader,紧接着再调用它的 Launch 函数,内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int MainDllLoader::Launch (HINSTANCE instance, base::TimeTicks exe_entry_point_ticks) const base::CommandLine& cmd_line = *base::CommandLine::ForCurrentProcess (); process_type_ = cmd_line.GetSwitchValueASCII (switches::kProcessType); ...... dll_ = Load (&file); if (!dll_) return chrome::RESULT_CODE_MISSING_DATA; OnBeforeLaunch (cmd_line, process_type_, file); DLL_MAIN chrome_main = reinterpret_cast <DLL_MAIN>(::GetProcAddress (dll_, "ChromeMain" )); int rc = chrome_main (instance, &sandbox_info, exe_entry_point_ticks.ToInternalValue ()); OnBeforeExit (file); return rc; }
这里完成了 chrome.dll 的载入,并且执行里面的 ChromeMain 函数。
3、ChromeMain() 函数 ChromeMain 函数负责 Embedder 层的实现类创建,并传递给 Content 层,定义在 chrome\app\chrome_main.cc 中,内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 extern "C" {DLLEXPORT int __cdecl ChromeMain (HINSTANCE instance, sandbox::SandboxInterfaceInfo* sandbox_info, int64_t exe_entry_point_ticks) } ...... #if defined(OS_WIN) DLLEXPORT int __cdecl ChromeMain (HINSTANCE instance, sandbox::SandboxInterfaceInfo* sandbox_info, int64_t exe_entry_point_ticks) #elif defined(OS_POSIX) int ChromeMain (int argc, const char ** argv) int64_t exe_entry_point_ticks = 0 ; #endif #if defined(OS_WIN) install_static::InitializeFromPrimaryModule (); #endif ChromeMainDelegate chrome_main_delegate ( base::TimeTicks::FromInternalValue(exe_entry_point_ticks)) content::ContentMainParams params (&chrome_main_delegate) ; ...... int rv = content::ContentMain (params); return rv; }
在ChromeMain中,最终执行到了 content::ContentMain 这个函数。
4、content::ContentMain() 函数 代码执行到这里,进入了 Content 层,并且传入参数 content::ContentMainParams 类型的参数 params,它是由 Embedder 层传递过来的重要参数,里面包含了 Embedder 层的具体实现信息,此结构体在 content\public\app\content_main.h 中定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 struct ContentMainParams { explicit ContentMainParams (ContentMainDelegate* delegate) : delegate(delegate) { } ContentMainDelegate* delegate; ......
其中有一个重要的成员变量 delegate,其类型为 content::ContentMainDelegate,它在 content\public\app\content_main_delegate.cc 中定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class CONTENT_EXPORT ContentMainDelegate { public : virtual ~ContentMainDelegate () {} virtual bool BasicStartupComplete (int * exit_code) virtual void PreSandboxStartup () virtual void SandboxInitialized (const std::string& process_type) virtual int RunProcess ( const std::string& process_type, const MainFunctionParams& main_function_params) virtual void ProcessExiting (const std::string& process_type) ...... virtual void PreCreateMainMessageLoop () ...... protected : friend class ContentClientInitializer ; virtual ContentBrowserClient* CreateContentBrowserClient () virtual ContentGpuClient* CreateContentGpuClient () virtual ContentRendererClient* CreateContentRendererClient () virtual ContentUtilityClient* CreateContentUtilityClient () };
可以看到,这里定义了一系列与启动相关的操作,并且通过几个 CreateXXX 的函数,获取 ContentBrowserClient、ContentRendererClient 等接口具体的实现,这也是 content API 的巧妙设计,通过这种方式,将浏览器的实现放入了 content 中。
继续往下看,content::ContentMain() 中调用了 content\app\content_main.cc 中的 service_manager::Main():
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int ContentMain (const ContentMainParams& params) ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate delegate (params) ; service_manager::MainParams main_params (&delegate) ; #if !defined(OS_WIN) && !defined(OS_ANDROID) main_params.argc = params.argc; main_params.argv = params.argv; #endif return service_manager::Main (main_params); }
在这里,使用一个 content::ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate 对象来构建了 main_params,并传入了 service_manager::Main()。
5、service_manager::Main 函数 service_manager::Main 函数位于 services\service_manager\embedder\main.cc,接收一个 MainParams 类型的参数,具体如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 int Main (const MainParams& params) MainDelegate* delegate = params.delegate; ...... ProcessType process_type = delegate->OverrideProcessType (); ...... static bool is_initialized = false ; #if !defined(OS_ANDROID) DCHECK (!is_initialized); #endif if (!is_initialized) { is_initialized = true ; ...... #if defined(OS_WIN) base::win::RegisterInvalidParamHandler (); ui::win::CreateATLModuleIfNeeded (); #endif ...... base::CommandLine::Init (argc, argv); ...... const auto & command_line = *base::CommandLine::ForCurrentProcess (); #if defined(OS_WIN) base::win::SetupCRT (command_line); #endif MainDelegate::InitializeParams init_params; ...... mojo::core::Init (mojo_config); ...... exit_code = delegate->Initialize (init_params); ...... } const auto & command_line = *base::CommandLine::ForCurrentProcess (); if (process_type == ProcessType::kDefault) { std::string type_switch = command_line.GetSwitchValueASCII (switches::kProcessType); if (type_switch == switches::kProcessTypeServiceManager) { process_type = ProcessType::kServiceManager; } else if (type_switch == switches::kProcessTypeService) { process_type = ProcessType::kService; } else { process_type = ProcessType::kEmbedder; } } switch (process_type) { case ProcessType::kDefault: NOTREACHED (); break ; case ProcessType::kServiceManager: exit_code = RunServiceManager (delegate); break ; case ProcessType::kService: CommonSubprocessInit (); exit_code = RunService (delegate); break ; case ProcessType::kEmbedder: if (delegate->IsEmbedderSubprocess ()) CommonSubprocessInit (); exit_code = delegate->RunEmbedderProcess (); break ; } ...... if (process_type == ProcessType::kEmbedder) delegate->ShutDownEmbedderProcess (); return exit_code; }
这里截取的代码比较长,也非常重要,我们主要关注这四个部分:
根据传入的 delegate 和 command_line 决定进程的类型
运行环境的初始化,比如 CreateATLModuleIfNeeded,SetupCRT 并用 is_initialized 来防止重复执行
通过传入的 delegate 进行程序的初始化操作,delegate->Initialize(init_params)
根据进程类型启动相应的工作
这里的 delegate 类型为 service_manager::MainDelegate*,是在 services/service_manager/embedder/main_delegate.h 中定义的抽象类,在这里我们主要关注它的 Initialize、RunEmbedderProcess 和 ShutDownEmbedderProcess,其中 Initialize 为被声明为纯虚函数,RunEmbedderProcess 和 ShutDownEmbedderProcess 又是什么都不做的,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class COMPONENT_EXPORT (SERVICE_MANAGER_EMBEDDER) MainDelegate public : virtual int Initialize (const InitializeParams& params) 0 ; ...... virtual int RunEmbedderProcess () ...... virtual void ShutDownEmbedderProcess ()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int MainDelegate::RunEmbedderProcess () return 0 ; } ... void MainDelegate::ShutDownEmbedderProcess ()
回到 service_manager::Main(),我们看到第一句 MainDelegate* delegate = params.delegate; 中的 params.delegate 就是前面在 content::ContentMain 中构建 main_params 所使用的 content::ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate 对象,因此,上述的三个函数 Initialize、RunEmbedderProcess、ShutDownEmbedderProcess 是由 ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate 来最终实现的,来看代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 int ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate::Initialize ( const InitializeParams& params) ...... return content_main_runner_->Initialize (content_main_params_); } ...... int ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate::RunEmbedderProcess () return content_main_runner_->Run (start_service_manager_only_); } ...... void ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate::ShutDownEmbedderProcess () #if !defined(OS_ANDROID) content_main_runner_->Shutdown (); #endif }
在这三个函数的定义中,都使用了 content_main_runner_ 这个成员变量来具体执行,它的定义为 std::unique_ptr<ContentMainRunnerImpl>。
6、整个程序的Runner,content::ContentMainRunnerImpl 这个 content::ContentMainRunnerImpl 是 content::ContentMainRunner 接口的一个实现,先来看接口的声明:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class CONTENT_EXPORT ContentMainRunner { public : virtual ~ContentMainRunner () {} static ContentMainRunner* Create () virtual int Initialize (const ContentMainParams& params) 0 ; virtual int Run (bool start_service_manager_only) 0 ; virtual void Shutdown () 0 ; };
再来看实现类的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class ContentMainRunnerImpl : public ContentMainRunner { public : static ContentMainRunnerImpl* Create () ContentMainRunnerImpl (); ~ContentMainRunnerImpl () override ; int TerminateForFatalInitializationError () int Initialize (const ContentMainParams& params) override int Run (bool start_service_manager_only) override void Shutdown () override ...... }
7、ContentMainRunner::Initialize() 函数 先来看 Initialize 函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 int ContentMainRunnerImpl::Initialize (const ContentMainParams& params) ui_task_ = params.ui_task; created_main_parts_closure_ = params.created_main_parts_closure; #if defined(OS_WIN) sandbox_info_ = *params.sandbox_info; #else ...... is_initialized_ = true ; delegate_ = params.delegate; ...... int exit_code = 0 ; if (delegate_->BasicStartupComplete (&exit_code)) return exit_code; completed_basic_startup_ = true ; ...... delegate_->PreSandboxStartup (); #if defined(OS_WIN) if (!InitializeSandbox ( service_manager::SandboxTypeFromCommandLine (command_line), params.sandbox_info)) return TerminateForFatalInitializationError (); #elif defined(OS_MACOSX) ...... #endif delegate_->SandboxInitialized (process_type); ...... return -1 ; }
大致看一下,在这个 Initialize 中,主要是根据 command_line 启动了相应的 sandbox service,并在启动前后都触发了 delegate_->PreSandboxStartup() 和 delegate_->SandboxInitialized(process_type),这个 delegate_ 来自于传入的 content::ContentMainParams 结构体,这个结构体是在 chrome_main.cc 中调用 content::ContentMain(params) 时所创建,所以这个 delegate_ 正是前面所提到的巧妙设计中,继承自 content::ContentMainDelegate 的 ChromeMainDelegate 对象,通过这一系列的调用,content 层就把创建 sandbox service 前后的事件触发了出来,具体实现者只要在 ChromeMainDelegate 中填充这两个时间点要做的事即可。
8、进程入口,ContentMainRunner::Run() 函数 再来看 Run 函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 int ContentMainRunnerImpl::Run (bool start_service_manager_only) ...... const base::CommandLine& command_line = *base::CommandLine::ForCurrentProcess (); std::string process_type = command_line.GetSwitchValueASCII (switches::kProcessType); ...... MainFunctionParams main_params (command_line) ; main_params.ui_task = ui_task_; main_params.created_main_parts_closure = created_main_parts_closure_; ...... if (process_type.empty ()) return RunServiceManager (main_params, start_service_manager_only); return RunOtherNamedProcessTypeMain (process_type, main_params, delegate_); }
此处先判断 process_type 是否为空,为空则代表当前执行的是默认进程(一般情况下为 Browser 进程),则调用 RunServiceManager(),否则调用 RunOtherNamedProcessTypeMain 根据process_type 来执行相应的进程。先来看 RunServiceManager:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 int ContentMainRunnerImpl::RunServiceManager (MainFunctionParams& main_params, bool start_service_manager_only) ...... if (!service_manager_context_) { ...... delegate_->PreCreateMainMessageLoop (); ...... delegate_->PostEarlyInitialization (main_params.ui_task != nullptr ); ...... } if (should_start_service_manager_only) return -1 ; is_browser_main_loop_started_ = true ; startup_data_ = std::make_unique <StartupDataImpl>(); startup_data_->thread = std::move (service_manager_thread_); startup_data_->service_manager_context = service_manager_context_.get (); main_params.startup_data = startup_data_.get (); return RunBrowserProcessMain (main_params, delegate_); }
同样,这里通过 delegate_ 做了一些操作之后,最后调用了 RunBrowserProcessMain() 函数,内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 int RunBrowserProcessMain (const MainFunctionParams& main_function_params, ContentMainDelegate* delegate) int exit_code = delegate->RunProcess ("" , main_function_params); #if defined(OS_ANDROID) return exit_code; #else if (exit_code >= 0 ) return exit_code; return BrowserMain (main_function_params); #endif }
非常简单明了,首先通过 delegate->RunProcess 把执行默认进程的优先权交由 Embedder 层,如果 Embedder 层成功执行了进程并最终返回了成功标志(exit_code >= 0),那么就退出函数;如果 Embedder 层对默认进程没有定义,就继续执行 content::BrowserMain,由此,Browser 进程开始执行。
再来看 RunOtherNamedProcessTypeMain 函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 int RunOtherNamedProcessTypeMain (const std::string& process_type, const MainFunctionParams& main_function_params, ContentMainDelegate* delegate) static const MainFunction kMainFunctions[] = { ...... {switches::kUtilityProcess, UtilityMain}, {switches::kRendererProcess, RendererMain}, {switches::kGpuProcess, GpuMain}, }; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < base::size (kMainFunctions); ++i) { if (process_type == kMainFunctions[i].name) { int exit_code = delegate->RunProcess (process_type, main_function_params); if (exit_code >= 0 ) return exit_code; return kMainFunctions[i].function (main_function_params); } } ...... return delegate->RunProcess (process_type, main_function_params); }
先建立了一个进程类型和入口函数指针的对应数组,再根据进程类型去具体执行,执行的过程与 Browser 进程一样,先通过 delegate->RunProcess 交由 Embedder 层处理,如果未处理再调用默认的进程入口函数,可以看到分别提供了 UtilityMain、RendererMain、GpuMain 这三个进程的入口,其中 RendererMain 则是我们关注的 Renderer 进程的入口函数,Renderer 进程从此处开始执行。最后一句,如果进程类型不在以上范围内,则交由 Embedder 去处理。
9、程序结束 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 void ContentMainRunnerImpl::Shutdown () DCHECK (is_initialized_); DCHECK (!is_shutdown_); if (completed_basic_startup_) { const base::CommandLine& command_line = *base::CommandLine::ForCurrentProcess (); std::string process_type = command_line.GetSwitchValueASCII (switches::kProcessType); delegate_->ProcessExiting (process_type); } #if !defined(CHROME_MULTIPLE_DLL_CHILD) BrowserTaskExecutor::Shutdown (); #endif #if defined(OS_WIN) #ifdef _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC _CrtDumpMemoryLeaks(); #endif #endif exit_manager_.reset (nullptr ); delegate_ = nullptr ; is_shutdown_ = true ; }
首先通过 delegate_->ProcessExiting(process_type) 通知 Embedder 层处理,然后做了一些善后释放的工作,最后将 is_shutdown_ 标记置为 true。
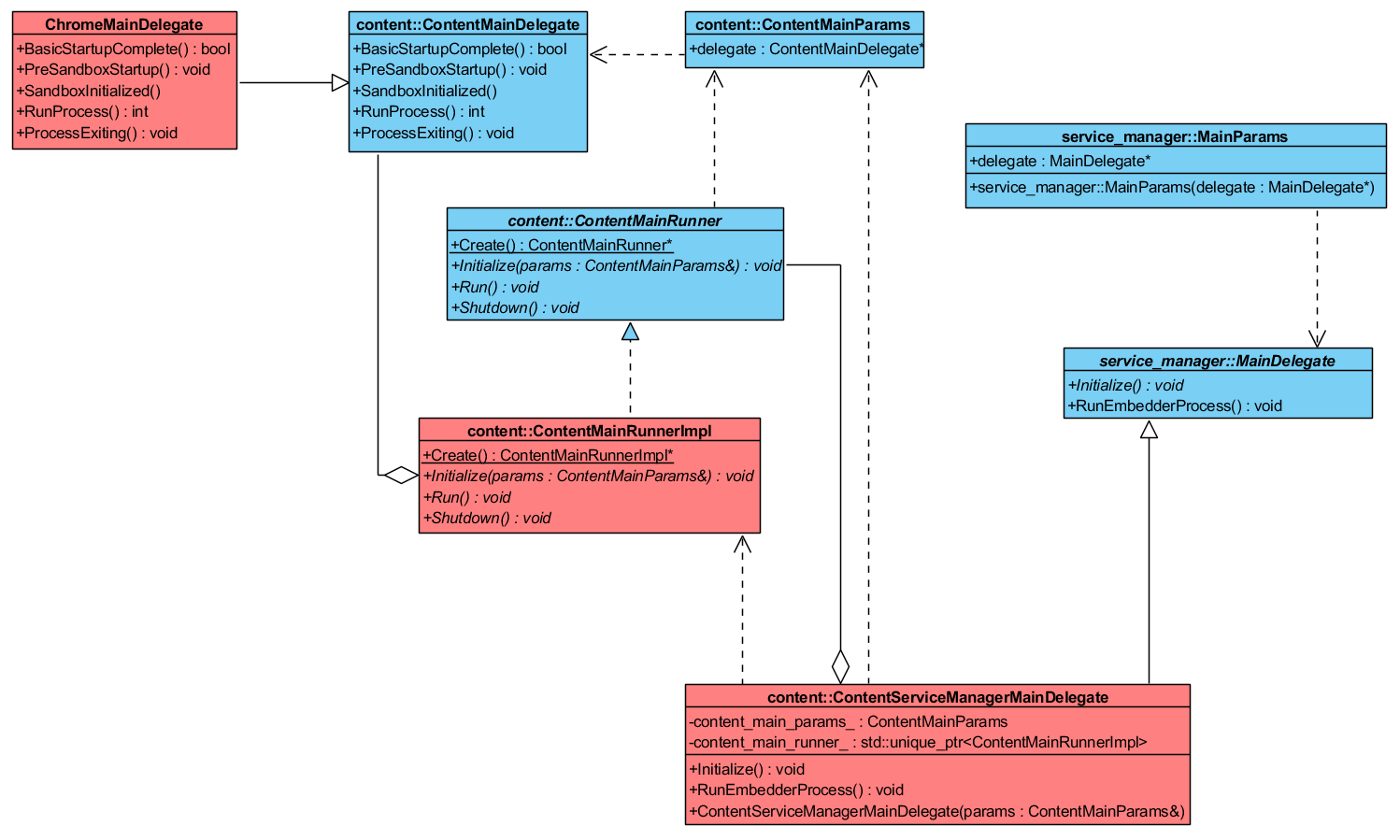
10、总结 前面分析了这么多,其实结合类图来看一下还是很简单明了的,主要起到作用的就是图中标红的三个,service_manager::Main 通过 content::ContentServiceManagerMainDelegate 的实例调用了 content::ContentMainRunnerImpl 实例中的 Initialize()、Run()、Shutdown() 函数,而在这个Runner中,又通过 content::ContentMainDelegate 接口指针调用到了由 Embedder 层创建的 ChromeMainDelegate 实例中的函数,由此完成了程序的启动以及 Content 层对 Embedder 的交互。